Blockchain technology is swiftly transforming the way we interact with digital data. It’s a secure, distributed ledger and record-keeping system that uses complex algorithms to store and transfer data in a decentralized way. Understanding blockchain technology can provide insights into how data and transactions are secured in the digital age.
This guide is designed to help beginners understand the basics of blockchain technology, how blockchain works, its various features, and potential applications. You’ll learn what makes blockchain so secure, the different types of blockchains that exist, the tools used to build them, and how they are used in various industries. By the end of this guide, you will have a better understanding of this revolutionary technology and how it is influencing change in our digital world.
What Is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that stores information in blocks of digital records. It is secure and incorruptible, so you can trust that the data stored on it is accurate and reliable. Each block in the chain contains information about the previous block or blocks, making it possible to trace back the chain’s history. In addition, blockchain technology is a decentralized database, meaning it is not dependent on any single system or authority to store or safeguard data.
The most well-known example of blockchain technology is Bitcoin, a digital currency created and maintained by a decentralized network of users. Each transaction between two parties using digital currency is recorded on the blockchain ledger and then validated by the entire network using secure cryptographic tools. This verification process ensures that all transactions are secure and valid. Not only does this make payments faster and more reliable, but it also eliminates the need for middlemen such as banks or credit card companies to validate transactions.
Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has some key benefits that are worth considering if you are thinking of incorporating it into your business. Firstly, it is extremely secure. Transactions on the blockchain are immutable, meaning they cannot be altered or tampered with, and they are time-stamped and visible on the public ledger.
Secondly, blockchain technology offers much greater efficiency, as transactions processed using blockchain records can be completed in a fraction of the time it typically takes for traditional methods. This improved efficiency also reduces transaction fees and improves accuracy of transaction records and data. Additionally, since blockchain-based transactions don’t require third parties to verify and process the information, there’s less risk of errors due to manual intervention.
Finally, using blockchain technology gives businesses the chance to reduce costs related to costly administration processes upon which they depend for data storage, processing and authentication of transactions. This level of proof of work, proof of work, proof of work and automation increases accuracy while cutting costs significantly.
What are the benefits of blockchain technology ?

Blockchain technology is a revolutionary concept that has gained a lot of attention in recent years. It was originally developed as the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its potential applications go far beyond just financial transactions.
A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger that records transactions in a decentralized and transparent manner. Rather than being controlled by a single entity or authority, the data on a blockchain is distributed across a network of computers and validated through a consensus mechanism. Here are some of the key benefits of blockchain technology:
Decentralization
One of the primary benefits of blockchain technology is its ability to enable decentralized networks. Rather than being controlled by a single entity, data on a blockchain is stored across a network of computers, each of which maintains an identical copy of the blockchain important or ledger. This means that no single entity has complete control over the data on the blockchain, which can increase transparency and eliminate the need for intermediaries to conduct transactions.
Decentralized networks can be particularly useful in industries like finance, where intermediaries like banks and other financial institutions often play a central role in transactions. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain technology can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and enable faster transactions.
Immutability
Another key benefit of blockchain technology is its immutability. Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without the consensus of the network. This means that data on a blockchain is highly secure and trustworthy, as there is no way to tamper with it without leaving a trace.
This feature of blockchain technology can be particularly useful in industries like supply chain management, where tracking the movement of goods and materials is essential. By recording the movement of goods on a public blockchain network, it becomes much more difficult for fraudsters to manipulate the supply chain.
Transparency
Blockchain technology also enables a high level of transparency. All participants in the network can view the data stored on the blockchain, which makes it easy to track and verify transactions. This transparency can be particularly useful in industries like finance, where it can help to prevent fraud and increase accountability.
Enhanced Security
Blockchain technology is also highly secure. Data on a blockchain is protected by cryptographic algorithms, which make it nearly impossible for hackers to access or manipulate the data. This makes blockchain technology particularly useful in industries like finance and healthcare, where the security of data is critical.
Faster and Cheaper Transactions
Blockchain technology can also enable faster and cheaper transactions. By eliminating intermediaries like banks and other financial institutions, blockchain technology can reduce the time and cost associated with transactions. This can be particularly useful in industries like cross-border payments, where traditional payment methods can be slow and expensive.
Improved Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology can also be used to improve supply chain management. By recording the movement of goods and materials on a blockchain, it becomes much easier to track the movement of goods and materials throughout the supply chain. This can help to reduce fraud and counterfeiting, improve traceability, and increase efficiency.
Increased Efficiency and Automation
Blockchain technology can also enable increased efficiency and automation. – Smart contract, contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, can automate many business processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency. This can be particularly useful in industries like real estate, where smart contracts can automate the process of buying and selling property.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Finally, blockchain technology can enable the creation of decentralized financial systems. Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is a growing industry that seeks to create financial systems that operate without intermediaries like banks. By using blockchain technology, DeFi systems can provide increased financial inclusion, reduce costs, and improve transparency.
What are the Benefits of Blockchains Over Traditional Finance?
Blockchains offer several key benefits that can’t be found in traditional finance systems. First and foremost, it is a secure, immutable and decentralized ledger. This means that no single entity can control or manipulate it – a huge advantage when it comes to security and preventing fraud. This also enables transparency within the blockchain system itself, allowing users to verify transactions without relying on a third party.
Additionally, blockchains have the potential to reduce costs dramatically by eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks and clearinghouses. This, blockchain users could save even more money in the long run since fewer intermediaries mean less overhead costs due to their reduced overhead expenses.
Finally, blockchains are more efficient than traditional finance systems since they are not limited by geographic location or time zones. Transactions can be completed much faster at minimal cost, even across international borders. This drastically reduces transaction fees and transaction times, making them more attractive for businesses of all sizes.
How is blockchain different from the cloud?

Blockchain is often compared to the cloud-based blockchain technologies, but they are not the same thing. Blockchain is different in several important ways.
Decentralized System
The key difference between bitcoin blockchain and systems and cloud technologies lies in their structure: the bitcoin blockchain and protocol is a decentralized system while cloud technologies are centralized. As a result, security and privacy protocols vary significantly between the two.
Data Security
In a blockchain system, data is secured across multiple computers rather than on one centralized server. This means that only multiple transactions, different parties can access the data stored on the blockchain, making it much harder for cyber criminals to access and use it maliciously.
Immutability
Another key difference lies in immutability of consortium blockchain: thanks to its distributed ledger technology (DLT), blockchain works because once data is added to the public blockchain itself, it cannot be changed or deleted without being recorded as a new transaction on a previous block of the ledger – something which makes it much more difficult for hackers to tamper with data stored on the blockchain.
Potential Applications of Blockchain in Various Industries
The potential applications of blockchain technology are vast, and it’s no secret that the emerging technology can revolutionize the way we as business network and approach virtually any industry you can think of.
Financial Services
One of the most obvious uses for a blockchain platform is in financial services. Blockchain technology can be used to securely record, transfer and store monetary transactions, allowing for faster payments with lower fees. Additionally, a blockchain platform offers the potential for new services to be developed on a decentralized platform – such as credit scoring or insurance services – which can help to reduce fraud and increase customer satisfaction.
Education
The education sector has already seen some applications of blockchain technology such as online textbooks that are stored on a distributed ledger or verified academic transcripts stored securely on a distributed ledger. Additionally, through smart contract, contracts can be used to manage enrollment processes and verify grades, ensuring that students have access to accurate records while ensuring they receive credit for their hard work.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, blockchain offers many benefits such as improved data security, quicker data sharing between patients and doctors and increased transparency when it comes to medical records. Additionally, smart contracts can be used to automate claims processing – resulting in faster payments and fewer mistakes – while also helping providers manage patient care more effectively.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
One of the most notable advantages of blockchain technology is the development of decentralized applications, or DApps. These applications are built on a distributed network and enable people to interact without the need for a centralized server or central authority anywhere.
The three primary components of DApps include:
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts that can be used to automate processes, enforce agreements, and store information securely on the blockchain.
- Decentralized Storage: This allows users to store data securely in a distributed manner, as opposed to centralized storage where data is stored in a single server.
- Decentralized Identities: This technology enables users to control their own identity information, as opposed to it being stored in a centralized database by an organization or government.
By removing the need for centralized control over applications and data, DApps offer greater security, transparency and privacy compared to traditional systems. Additionally, these applications reduce processing fees by eliminating intermediaries and create new business opportunities by removing barriers between producers and consumers.
Challenges and Risks Associated With Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology is not without its challenges and risks. To make informed decisions about using a blockchain platform for your business, it’s important to consider the following potential problems.
Security Vulnerabilities
As with any technology, there are security vulnerabilities that may be exposed in private blockchain networks. If a hacker is able to access the private key or keys or gain control of a node in the private blockchain network, they could be able to alter transactions or compromise data. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, so do the methods used by hackers to exploit its weaknesses.
Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks can only process a certain number of transactions per second, which can create scalability issues if there is high demand. To address these issues, developers have proposed various solutions such as sharding or sidechains which can help reduce the strain on the bitcoin network and increase its capacity.
High Energy Consumption
The consensus algorithms used by many blockchain applications and networks require a large amount of computing power, which can lead to high energy consumption and a significant environmental impact if not managed properly. To reduce their energy consumption and associated costs, blockchain mining companies are exploring more efficient consensus algorithms and other innovative methods for reducing their carbon footprint.
Why is blockchain important?
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize how we transfer, store, and use data. Its implications for financial transactions and recordkeeping are particularly exciting, as blockchain offers a secure, immutable form of record-keeping that is completely decentralized.
What makes blockchain protocols and it so important is that it enables two or more parties to send and receive digital assets in a secure and transparent way without the need for intermediaries. This can be applied to anything from storing data sharing sensitive medical records between doctors to using blockchain protocols for digital assets and exchanging bitcoin mining cryptocurrencies between buyers and sellers.
Furthermore, blockchain technology allows users to have control over their data without requiring a centralized third-party. It also allows for faster transfer times since there is no need for intermediaries to approve transfers or process them manually. Finally, because of its distributed nature, a blockchain database is much less susceptible to hacking than traditional centralized databases.
In short, with blockchain implementation and its powerful combination of security, decentralization and speed, blockchain technology has the power to change the way we do business in many different industries.
What are the types of blockchain networks?
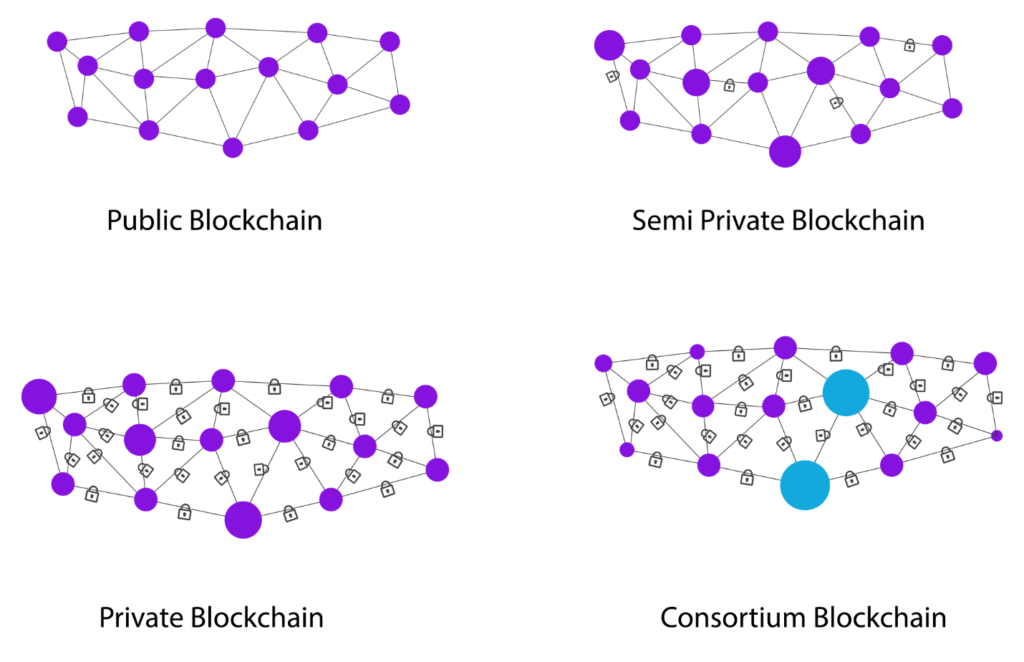
There are generally three types of blockchain networks: public, private, and consortium.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains, also known as permissionless blockchains, are open networks where anyone can join and participate in the network without the need for permission. These networks are completely decentralized, meaning that there is no central authority controlling the network. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other popular cryptocurrencies operate on public blockchains.
In public blockchains, anyone can read, write, or execute smart contracts on the network. These networks offer a high level of transparency, immutability, and security, but they are also slower and less scalable than a private blockchain, or consortium blockchains due to the large number of participants.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are networks that require permission to join and participate. These networks are typically owned and operated by a single entity, such as a company or organization, and are designed to be used for specific purposes or applications. Private blockchains offer higher scalability, faster transactions, and better privacy than public blockchains.
In private blockchains, access to the network is restricted to a select group of participants, which means that there is a higher level of control over the decentralized network itself’s security and governance. Private blockchains are commonly used by enterprises to create secure and efficient systems for tracking supply chains, managing customer data, and more.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are a hybrid of public and private blockchains. They are typically owned and operated by a consortium of companies or organizations that collaborate to create a shared blockchain network. Consortium blockchains offer the benefits of both public and private blockchains, including decentralization, security, and transparency.
In consortium blockchains, access and private key and to the network is restricted to a group of approved participants who have been granted permission to join and use the network. This type of consortium blockchain network is commonly used in industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics to create shared platforms for secure and efficient data sharing and collaboration.
Blockchain vs. Banks
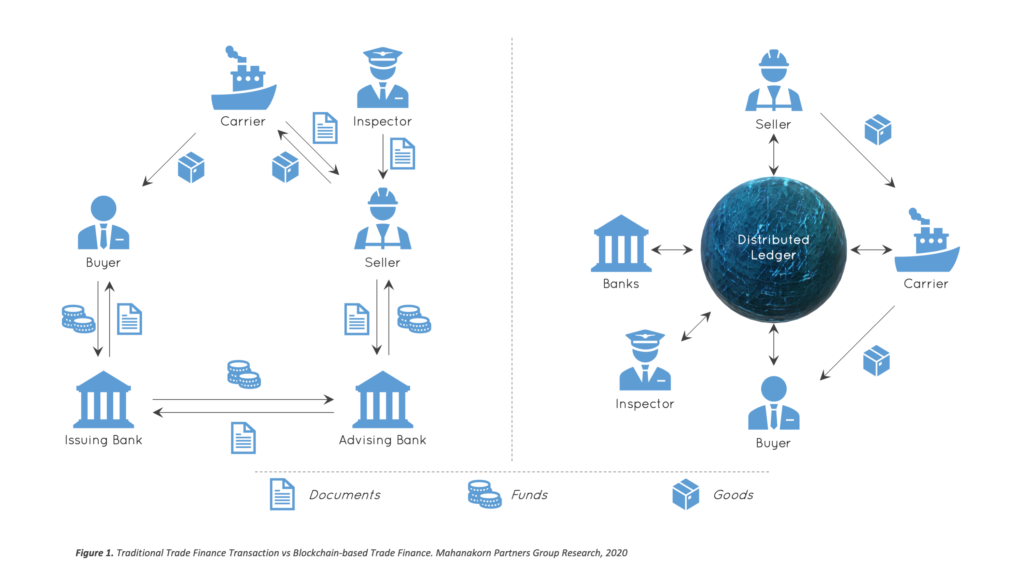
The banking sector has been the traditional method for making and recording financial transactions for decades. With the invention of blockchain technology, things are beginning to change.
Now, let’s explore some key differences between banks and blockchain technology:
Decentralization
One of the most significant differences between blockchain systems and banks is their degree of centralization. Banks are centralized institutions that control the flow of money in the financial system. They act as intermediaries between individuals and businesses, holding and transferring funds on their behalf. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, is decentralized. Rather than being controlled by a single entity, data on a blockchain is stored across a network of computers, each of which maintains an identical copy of the ledger. This means that no single entity has complete control over the data on the entire blockchain itself, which can increase transparency and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
Immutability
Another key difference between the blockchain platforms and banks is their approach to data integrity. Banks rely on centralized databases to store and manage financial transactions. While these databases are secured with encryption and other security measures, they are still vulnerable to data breaches, hacking, and other forms of cyberattacks.
Blockchain technology, on the other hand, uses a distributed ledger technology that is virtually immutable. Each transaction on blockchain nodes is verified and recorded by multiple nodes on the network, and once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This makes it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the data on a blockchain, as they would need to hack into multiple nodes on the network simultaneously.
Speed and Efficiency
Banks can be slow and inefficient when it comes to processing transactions, particularly international transfers that require intermediaries and can take several days to complete. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, can enable near-instantaneous transactions that can be completed in a matter of seconds. This is because blockchain transactions are processed directly between peers on the bitcoin network itself, eliminating the need for intermediaries and streamlining the process.
Privacy
One potential downside of blockchain technology is its lack of privacy. While transactions on a blockchain are completely transparent, the identities of the parties involved are often anonymous. This can be a concern for businesses and individuals who value privacy and confidentiality in their financial transactions. Banks, on the other hand, have strict privacy policies and regulations in place to protect their customers’ personal and financial information.
Regulation
Another key difference between blockchain platforms and banks is their regulatory frameworks. Banks are heavily regulated by governments and financial authorities, which can help protect consumers and maintain the stability of the financial system. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, is still in its early stages, and there are few regulations in place to govern its use. This can make it difficult for businesses and individuals to navigate the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain adoption.
How do different industries use blockchain?

Blockchain technology can be used in a variety of different industries to enhance security, increase efficiency, record transactions, and facilitate easier data access. Because the blockchain protocol is based on distributed ledgers, it is well-suited for companies that need to effectively store and share large amounts of data across multiple platforms.
Some of the most popular industries that make use of blockchain technology include:
- Financial services: Banks and other financial institutions use blockchain technology to store and track sensitive customer data, as well as to facilitate payments both domestically and internationally.
- Healthcare: By implementing blockchain technology into healthcare systems, doctors, nurses, and patients can securely access necessary medical information in real-time.
- Government: Blockchain can help governments streamline administrative processes such as tax reporting, identity verifications, and land title registrations.
- Logistics: Blockchain technology has the potential to optimize supply chain management by increasing transparency throughout the process.
- Education: Blockchain can be used in the educational system to store student records safely and accurately without the need for third-party verification.
In addition to blockchain work in these industries, many other businesses are exploring how they can leverage the power of blockchain for their operations.
FAQs
The blockchain is a complex and intricate technology, but understanding the basics can help you get a better grasp on what is blockchain and how it works. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about what is blockchain and how does blockchain work now:
Is Blockchain Secure?
Yes. The decentralized nature of the blockchain protocol makes it secure by creating an unalterable, distributed digital ledger for data storage recording transactions. Every transaction on the blockchain network is encrypted using advanced cryptography and stored in a shared record that cannot be altered or tampered with.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are programmed to automatically execute when certain conditions are met. They are often used in blockchain applications to automate and streamline complex business processes.
How Can I Use Blockchain Technology?
There are many ways to use blockchain technology, from developing your own decentralized applications (dApps) on existing blockchain infrastructure and platforms to investing in different blockchains and cryptocurrencies. You can also develop blockchain applications and also use blockchain technology to improve existing processes or create new ones within your organization or industry.
What is the difference between a public and a private blockchain?
A public blockchain is open to anyone, while a private blockchain is restricted to a specific group of users. Public blockchains are typically used for cryptocurrencies, while private blockchains are used for enterprise applications that require greater control and privacy.
What are the challenges facing blockchain adoption?
The challenges facing blockchain adoption include regulatory uncertainty, scalability issues, interoperability challenges, and the need for greater education and awareness about the technology.
What is a fork in blockchain?
A fork in blockchain occurs when there is a disagreement among the network participants about the rules of the blockchain. This can result in the creation of a new blockchain, with the original blockchain continuing to exist as well.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is an incredibly powerful tool and it’s here to stay. It’s a clever way of decentralizing data, making it secure and removing the need for a third party to financially validate transactions in bitcoin transactions. It’s important to note that the bitcoin blockchain is dynamic and constantly evolving, both in terms of its underlying technology and its applications.
For those just getting started with blockchain strategy, it’s essential to understand blockchain’s inner workings, how it fits into the global economy, and how it could change the future of finance record transactions and data storage. With its potential for secure, transparent transactions and digital information, the blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the way we store, transfer and use data. Whether you’re a businessperson, a developer or an enthusiast, the blockchain has something to offer you.

